Visual Glossary Of Container Technology
This post is simply about maintaining a visual glossary of container technology.
Docker
Containers and Virtual Machines
Containers
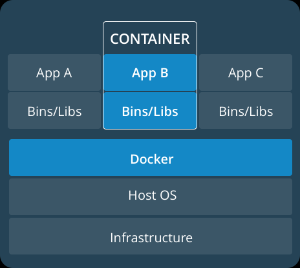
Containers are an abstraction at the app layer that packages code and dependencies together. Multiple containers can run on the same machine and share the OS kernel with other containers, each running as isolated processes in user space. Containers take up less space than VMs (container images are typically tens of MBs in size), and start almost instantly.
Virtual Machines
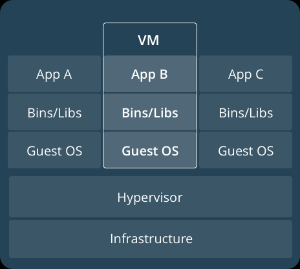
Virtual machines (VMs) are an abstraction of physical hardware turning one server into many servers. The hypervisor allows multiple VMs to run on a single machine. Each VM includes a full copy of an operating system, one or more apps, necessary binaries and libraries - taking up tens of GBs. VMs can also be slow to boot.
Containers and Virtual Machines Together
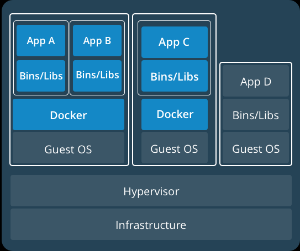
There is nothing preventing containers and virtual machines from working together in order to provide further isolation from each others. This is particularly useful in a multi-tenants scenario where the infrastructure is shared among many unrelated tenants in order to maximize the use of the infrastructure in question. From https://www.docker.com/what-container
Kubernetes
Pods and Nodes
Pods
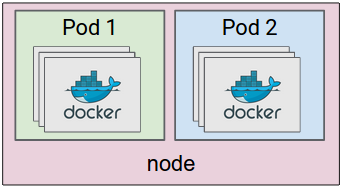
A pod (as in a pod of whales or pea pod) is a group of one or more containers (such as Docker containers), with shared storage/network, and a specification for how to run the containers. A pod’s contents are always co-located and co-scheduled, and run in a shared context. A pod models an application-specific “logical host” - it contains one or more application containers which are relatively tightly coupled — in a pre-container world, they would have executed on the same physical or virtual machine.
Nodes
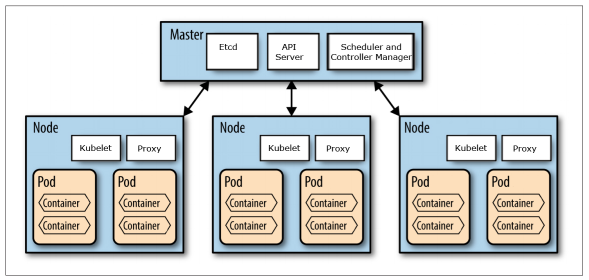
A node is a worker machine in Kubernetes, previously known as a minion. A node may be a VM or physical machine, depending on the cluster. Each node has the services necessary to run pods and is managed by the master components. The services on a node include Docker, kubelet and kube-proxy. From https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/


Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *